CIT clinical data when compared to total tonsillectomy
Clinical data from systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 studies. CIT (n-1996) versus (n=2195)
-
Reduction in pain
0days sooner pain free. Less pain @ 1 day and 1 week.
-
Reduction in time to analgesia free
0days sooner
-
Reduction in risk of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage
0%less likely to have PTH
-
Faster return to normal activity
0days sooner
-
Faster return to normal diet
0days sooner
-
Low rate of revision
0%reoperation at 5 years
Intracapsular tonsillectomy and total tonsillectomy clinical data
-

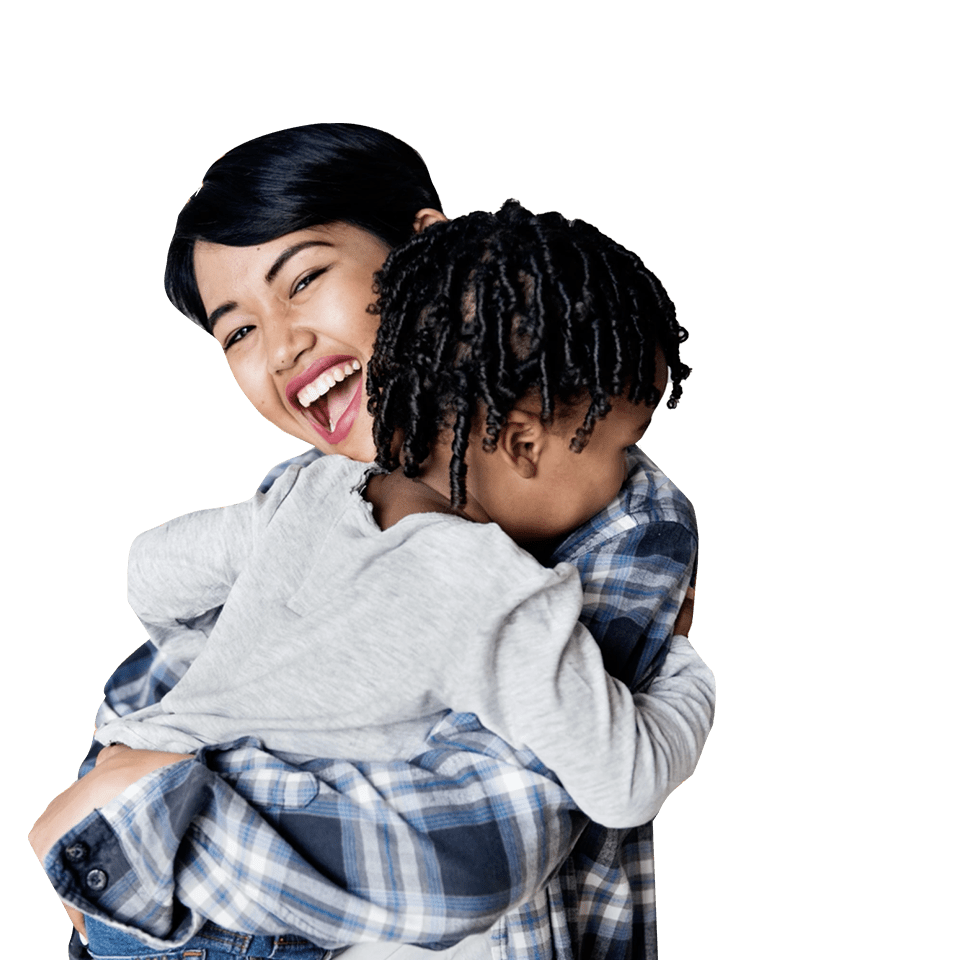
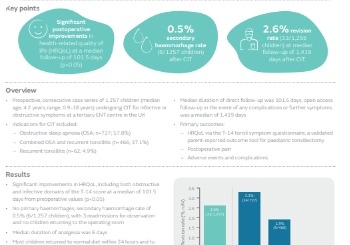
COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectomy (CIT): a prospective series of 1,257 paediatric cases with long-term follow-up
Prospective, consecutive case series of 1,257 children undergoing CIT for infective or obstructive symptoms
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

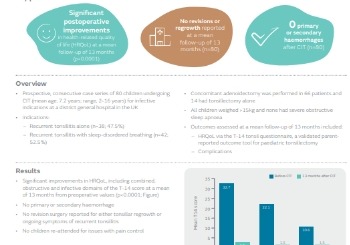
COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectomy (CIT) in children with recurrent tonsillitis: Initial experience
Prospective, consecutive case series of 80 children undergoing CIT for infective indications.
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectomy compared with total tonsillectomy: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectoy (CIT) delivers low morbidity and return to theatre rates and low rates of re-operation in pediatric population
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

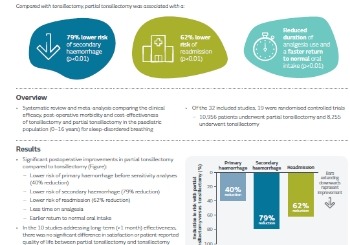
Partial tonsillectomy results in fewer postoperative complications compared to tonsillectomy
Systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the clinical efficacy, post-operative morbidity and cost-effectiveness of tonsillectomy and partial tonsillectomy in the pediatri
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

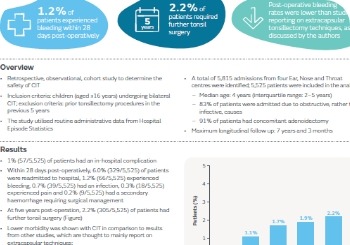
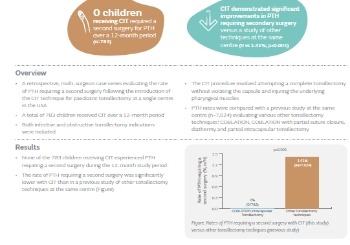
Rates of post-tonsillectomy haemmorhage (PTH) requiring second surgery in 783 children receiving COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectomy
A retrospective, multi-surgeon case series evaluating the rate of PTH requiring a second surgery following the introduction of the CIT technique for pediatric tonsillectomy at
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

Systematic Literature Review
COBLATION Intracapsular Tonsillectomy compared with total tonsillectomy: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read -

Postoperative Bleeding and Associated Utilization following Tonsillectomy in Children
A systematic review and meta-analysis analyzing the rates of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage (PTH) among the most commonly used techniques.
Reading Time: < 1 minute Read
No matter how statistically safe a procedure has proven to be, every surgery has risks. Post Tonsillectomy Hemorrhage (PTH) is a potentially serious complication that has been reported in literature for both adult and pediatric patients. It is reported to occur following use of COBLATION devices as well as following the use of other surgical devices and methods. Before making any surgical decision, you should speak with your doctor about any potential risks.
COBLATION wands are contraindicated for use in patients with cardiac pacemakers or other electronic device implants.
- Smith+Nephew 2024. Clinical publications on ENT COBLATION. EA/ENT/COBLATION/004/v1.
- Smith+Nephew 2021. Partial tonsillectomy using COBLATION versus alternative tonsillectomy techniques: A systematic literature review with meta-analysis. Internal Report. EA/ENT/COBLATION/002/V4.
- Amin N, Bhargava E, Prentice JG, Shamil E, Walsh M, Tweedie DJ. Coblation Intracapsular Tonsillectomy in Children: A Prospective Study of 1257 Consecutive Cases with Long Term Follow Up. Clin Otolaryngol. 2021;00:1 – 9.
- Francis DO, Fonnesbeck C, Sathe N, McPheeters M, Krishnaswami S, Chinnadurai S. Postoperative Bleeding and Associated Utilization Following Tonsillectomy in Children: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;156:442 – 455.
- Varadharajan K, Caton N, Faulkner J, Khemani S. Coblation® intracapsular tonsillectomy in children with recurrent tonsillitis: Initial experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;135:110113.
- Chau SM, Sharma GK, Ahuja GS, Huoh KC, Pham NS. Post-Operative Hemorrhage Rates in Coblation Intracapsular Tonsillectomy: A 6-year Experience. Poster presented at: Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings (COSM)2019; Austin, Texas.
- Albright JT, Duncan NO, Smerica AM, Edmonds JL. Intra-capsular complete tonsillectomy, a modification of surgical technique to eliminate delayed post-operative bleeding. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;128:109703.
- Keltie K, Donne A, Daniel M, et al. Paediatric tonsillectomy in England: A cohort study of clinical practice and outcomes using Hospital Episode Statistics data (2008-2019). Clin Otolaryngol. 2021;00:1–10.
;)